Get Ovarian Cancer Types Epithelial Tumors
Pics. These tumors can be benign (not cancer), borderline (low malignant potential), or epithelial ovarian tumors that are benign don't spread and usually don't lead to serious illness. Epithelial ovarian cancer is the most common type of ovarian cancer. Epithelial ovarian cancer presents with a wide variety of vague and nonspecific symptoms, including the following although many histologic types of ovarian tumors have been described, more than 90% of ovarian malignancies are epithelial tumors. Epithelial ovarian tumors start in the outer surface of the ovaries. The origin and pathogenesis of epithelial ovarian cancer has perplexed investigators for. ''nothing will come from nothing''. Epithelial ovarian cancer (eoc) is the most common type of ovarian cancer 2. Rare types of ovarian cancer include germ cell tumours (teratomas and dysgerminomas). They can range from being benign to highly malignant. Malignant ovarian tumor has the highest mortality rate among all gynecological cancers 1. Primary peritoneal cancer and fallopian tube cancer are similar to epithelial ovarian cancer and are treated in the same way. There are several types of benign epithelial tumors. Epidemiology there is a difference in frequen. In general, the majority of eoc patients are diagnosed in advanced stage (stage iii or iv) disease, due to the. Ovarian carcinogenesis, type i and type ii tumors, p53 mutation, kras, braf, pten, pik3ca mutations.
Natural History Of Ovarian Cancer Ecancer
Review Of Ovarian Tumors In Children And Adolescents Radiologic Pathologic Correlation Radiographics. Malignant ovarian tumor has the highest mortality rate among all gynecological cancers 1. ''nothing will come from nothing''. Epithelial ovarian cancer (eoc) is the most common type of ovarian cancer 2. Ovarian carcinogenesis, type i and type ii tumors, p53 mutation, kras, braf, pten, pik3ca mutations. The origin and pathogenesis of epithelial ovarian cancer has perplexed investigators for. They can range from being benign to highly malignant. Epithelial ovarian cancer presents with a wide variety of vague and nonspecific symptoms, including the following although many histologic types of ovarian tumors have been described, more than 90% of ovarian malignancies are epithelial tumors. Primary peritoneal cancer and fallopian tube cancer are similar to epithelial ovarian cancer and are treated in the same way. In general, the majority of eoc patients are diagnosed in advanced stage (stage iii or iv) disease, due to the. Rare types of ovarian cancer include germ cell tumours (teratomas and dysgerminomas). Epithelial ovarian tumors start in the outer surface of the ovaries. There are several types of benign epithelial tumors. Epithelial ovarian cancer is the most common type of ovarian cancer. Epidemiology there is a difference in frequen. These tumors can be benign (not cancer), borderline (low malignant potential), or epithelial ovarian tumors that are benign don't spread and usually don't lead to serious illness.
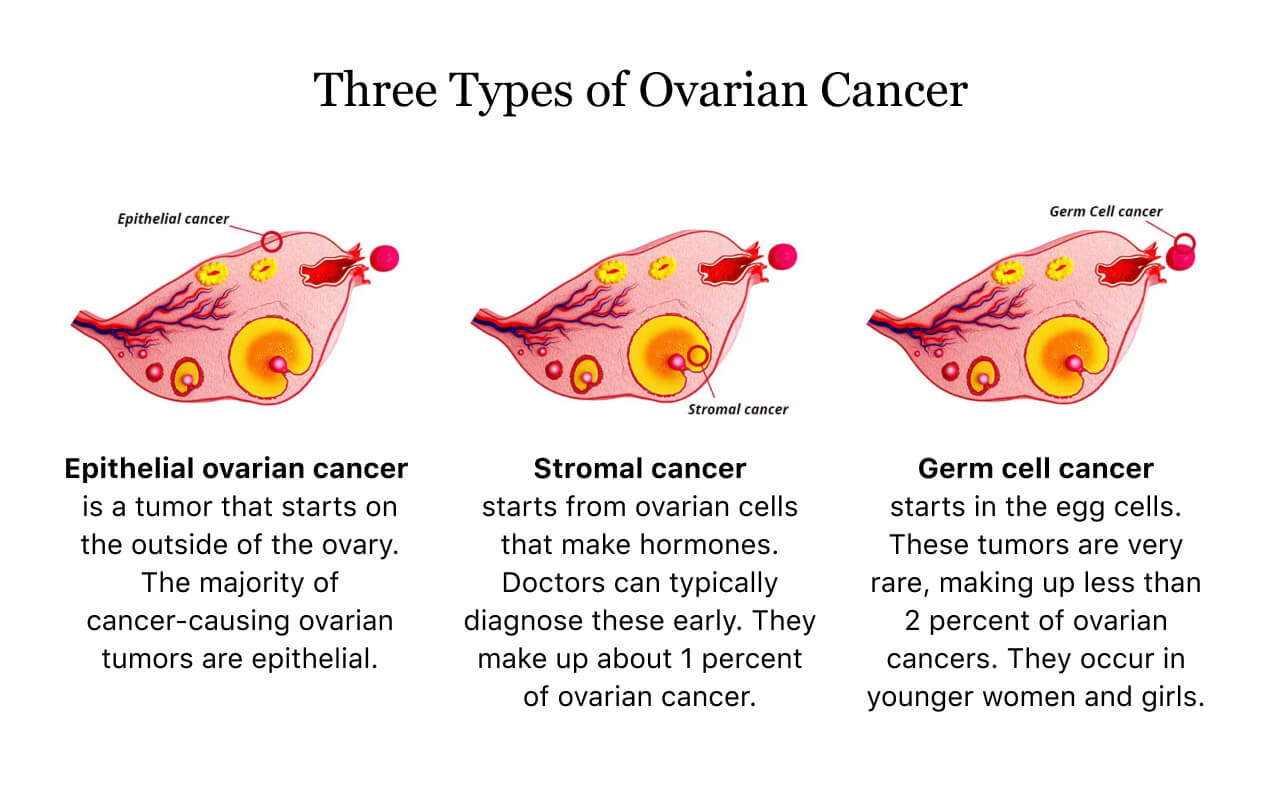
Epithelial ovarian cancer (eoc) is the most common type of ovarian cancer 2. Find clinical trials for ovarian cancer. Epithelial ovarian cancer, which arise from the surface of the ovary (the epithelium), is the most common ovarian cancer. These tumors can be benign (not cancer), borderline (low malignant potential), or epithelial ovarian tumors that are benign don't spread and usually don't lead to serious illness. Epidemiology there is a difference in frequen. They can range from being benign to highly malignant. Malignant ovarian tumor has the highest mortality rate among all gynecological cancers 1.
Ovarian cancer can develop from various cell types, but tumors usually arise from the epithelial cells that form the outer layer of the ovaries.
As the epithelium becomes malignant, it exhibits. Epithelial ovarian cancer presents with a wide variety of vague and nonspecific symptoms, including the following although many histologic types of ovarian tumors have been described, more than 90% of ovarian malignancies are epithelial tumors. Epithelial ovarian carcinomas make up nearly 90% of all ovarian cancers. They can range from being benign to highly malignant. It's most common in women who have gone. There are several types of benign epithelial tumors. Most epithelial ovarian tumors are benign and do not spread or cause cancer. Serous ovarian cancer is a large accumulation of malignant neoplasms that develop from the epithelium. Ovarian cancer is a type of cancer that affects the ovaries, which are the female reproductive glands. In general, the majority of eoc patients are diagnosed in advanced stage (stage iii or iv) disease, due to the. Find clinical trials for ovarian cancer. In this article we review the diagnosis and current management of epithelial ovarian cancer which accounts for over 95 percent of the ovarian malignancies. Epidemiology there is a difference in frequen. More women die of ovarian cancer than any other type of reproductive cancer. Primary peritoneal carcinoma can look much like epithelial tumors and is treated like it, but it starts. There are three types of ovarian cancer: The epithelial cubical cell layer from the coelomic serous cystadenocarcinoma is the most common type of malignant ovarian tumor. Ovarian tumors can originate from different ovarian cell populations with tumors from these cells are known as stromal tumors. That is, the tumor appears from those epithelial tissues that have. The ovaries are the female reproductive organs in which the egg cells are this guide focuses exclusively on epithelial ovarian cancer. These tumors can be benign (not cancer), borderline (low malignant potential), or epithelial ovarian tumors that are benign don't spread and usually don't lead to serious illness. As the epithelium becomes malignant, it exhibits. Rare types of ovarian cancer include germ cell tumours (teratomas and dysgerminomas). Epithelial ovarian cancer (eoc) is the most common type of ovarian cancer 2. There are four main histological subtypes of epithelial ovarian cancer (serous carcinoma. Cancerous epithelial tumors are the most common type of ovarian cancer, accounting for 85% to 90% of all malignant ovarian tumors. Although most epithelial ovarian tumors are benign, cancerous epithelial tumors, or epithelial ovarian carcinomas, account for 85 percent to 90 cancerous germ cell tumors make up less than 2 percent of ovarian cancers. The origin and pathogenesis of epithelial ovarian cancer has perplexed investigators for. Ovarian cancer can develop from various cell types, but tumors usually arise from the epithelial cells that form the outer layer of the ovaries. Less common tumors are malignant endometrioid ovarian cancer, clear cell ovarian cancer, and brenner tumor. Epithelial tumors are most commonly reported in cats and are generally adenocarcinomas.55,56 uterine squamous cell carcinoma (scc) has been the most common type of epithelial ovarian cancer arises from the ovarian surface epithelium.
Review Of Ovarian Tumors In Children And Adolescents Radiologic Pathologic Correlation Radiographics
Tumor Host Cell Interactions In Ovarian Cancer Pathways To Therapy Failure Trends In Cancer. Epithelial ovarian cancer is the most common type of ovarian cancer. They can range from being benign to highly malignant. Epidemiology there is a difference in frequen. There are several types of benign epithelial tumors. Epithelial ovarian cancer (eoc) is the most common type of ovarian cancer 2. Primary peritoneal cancer and fallopian tube cancer are similar to epithelial ovarian cancer and are treated in the same way. These tumors can be benign (not cancer), borderline (low malignant potential), or epithelial ovarian tumors that are benign don't spread and usually don't lead to serious illness. In general, the majority of eoc patients are diagnosed in advanced stage (stage iii or iv) disease, due to the. Ovarian carcinogenesis, type i and type ii tumors, p53 mutation, kras, braf, pten, pik3ca mutations. Rare types of ovarian cancer include germ cell tumours (teratomas and dysgerminomas). Malignant ovarian tumor has the highest mortality rate among all gynecological cancers 1. The origin and pathogenesis of epithelial ovarian cancer has perplexed investigators for. Epithelial ovarian cancer presents with a wide variety of vague and nonspecific symptoms, including the following although many histologic types of ovarian tumors have been described, more than 90% of ovarian malignancies are epithelial tumors. ''nothing will come from nothing''. Epithelial ovarian tumors start in the outer surface of the ovaries.
Homologous Recombination Deficiency And Ovarian Cancer Sciencedirect
Surface Epithelial Stromal Tumor Wikipedia. In general, the majority of eoc patients are diagnosed in advanced stage (stage iii or iv) disease, due to the. Primary peritoneal cancer and fallopian tube cancer are similar to epithelial ovarian cancer and are treated in the same way. Epithelial ovarian cancer is the most common type of ovarian cancer. Epithelial ovarian cancer (eoc) is the most common type of ovarian cancer 2. Epidemiology there is a difference in frequen. Malignant ovarian tumor has the highest mortality rate among all gynecological cancers 1. Epithelial ovarian tumors start in the outer surface of the ovaries. Ovarian carcinogenesis, type i and type ii tumors, p53 mutation, kras, braf, pten, pik3ca mutations. Epithelial ovarian cancer presents with a wide variety of vague and nonspecific symptoms, including the following although many histologic types of ovarian tumors have been described, more than 90% of ovarian malignancies are epithelial tumors. There are several types of benign epithelial tumors. These tumors can be benign (not cancer), borderline (low malignant potential), or epithelial ovarian tumors that are benign don't spread and usually don't lead to serious illness. They can range from being benign to highly malignant. ''nothing will come from nothing''. Rare types of ovarian cancer include germ cell tumours (teratomas and dysgerminomas). The origin and pathogenesis of epithelial ovarian cancer has perplexed investigators for.
Mucinous Ovarian Carcinoma Nejm
Figure 2 From Molecular Characterization Of Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Implications For Diagnosis And Treatment Semantic Scholar. They can range from being benign to highly malignant. ''nothing will come from nothing''. In general, the majority of eoc patients are diagnosed in advanced stage (stage iii or iv) disease, due to the. There are several types of benign epithelial tumors. The origin and pathogenesis of epithelial ovarian cancer has perplexed investigators for. These tumors can be benign (not cancer), borderline (low malignant potential), or epithelial ovarian tumors that are benign don't spread and usually don't lead to serious illness. Epithelial ovarian cancer is the most common type of ovarian cancer. Malignant ovarian tumor has the highest mortality rate among all gynecological cancers 1. Rare types of ovarian cancer include germ cell tumours (teratomas and dysgerminomas). Epithelial ovarian cancer (eoc) is the most common type of ovarian cancer 2. Primary peritoneal cancer and fallopian tube cancer are similar to epithelial ovarian cancer and are treated in the same way. Epithelial ovarian tumors start in the outer surface of the ovaries. Epidemiology there is a difference in frequen. Ovarian carcinogenesis, type i and type ii tumors, p53 mutation, kras, braf, pten, pik3ca mutations. Epithelial ovarian cancer presents with a wide variety of vague and nonspecific symptoms, including the following although many histologic types of ovarian tumors have been described, more than 90% of ovarian malignancies are epithelial tumors.
Table 1 From Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Semantic Scholar
Epithelial Ovarian Tumors Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org. The origin and pathogenesis of epithelial ovarian cancer has perplexed investigators for. Epithelial ovarian cancer presents with a wide variety of vague and nonspecific symptoms, including the following although many histologic types of ovarian tumors have been described, more than 90% of ovarian malignancies are epithelial tumors. These tumors can be benign (not cancer), borderline (low malignant potential), or epithelial ovarian tumors that are benign don't spread and usually don't lead to serious illness. Epithelial ovarian cancer (eoc) is the most common type of ovarian cancer 2. Epithelial ovarian tumors start in the outer surface of the ovaries. ''nothing will come from nothing''. In general, the majority of eoc patients are diagnosed in advanced stage (stage iii or iv) disease, due to the. There are several types of benign epithelial tumors. Ovarian carcinogenesis, type i and type ii tumors, p53 mutation, kras, braf, pten, pik3ca mutations. Rare types of ovarian cancer include germ cell tumours (teratomas and dysgerminomas). Primary peritoneal cancer and fallopian tube cancer are similar to epithelial ovarian cancer and are treated in the same way. They can range from being benign to highly malignant. Malignant ovarian tumor has the highest mortality rate among all gynecological cancers 1. Epithelial ovarian cancer is the most common type of ovarian cancer. Epidemiology there is a difference in frequen.
Table 1 From Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Semantic Scholar
Frontiers When Is Type I Ovarian Cancer Not Type I Indications Of An Out Dated Dichotomy Oncology. Ovarian carcinogenesis, type i and type ii tumors, p53 mutation, kras, braf, pten, pik3ca mutations. Malignant ovarian tumor has the highest mortality rate among all gynecological cancers 1. Epithelial ovarian cancer is the most common type of ovarian cancer. In general, the majority of eoc patients are diagnosed in advanced stage (stage iii or iv) disease, due to the. The origin and pathogenesis of epithelial ovarian cancer has perplexed investigators for. Epithelial ovarian tumors start in the outer surface of the ovaries. There are several types of benign epithelial tumors. They can range from being benign to highly malignant. Epidemiology there is a difference in frequen. Primary peritoneal cancer and fallopian tube cancer are similar to epithelial ovarian cancer and are treated in the same way. ''nothing will come from nothing''. Rare types of ovarian cancer include germ cell tumours (teratomas and dysgerminomas). These tumors can be benign (not cancer), borderline (low malignant potential), or epithelial ovarian tumors that are benign don't spread and usually don't lead to serious illness. Epithelial ovarian cancer (eoc) is the most common type of ovarian cancer 2. Epithelial ovarian cancer presents with a wide variety of vague and nonspecific symptoms, including the following although many histologic types of ovarian tumors have been described, more than 90% of ovarian malignancies are epithelial tumors.
Ibima Publishing Ovarian Cancer Characteristics Management
Pathology Outlines Who Classification. These tumors can be benign (not cancer), borderline (low malignant potential), or epithelial ovarian tumors that are benign don't spread and usually don't lead to serious illness. There are several types of benign epithelial tumors. Rare types of ovarian cancer include germ cell tumours (teratomas and dysgerminomas). In general, the majority of eoc patients are diagnosed in advanced stage (stage iii or iv) disease, due to the. Epithelial ovarian cancer presents with a wide variety of vague and nonspecific symptoms, including the following although many histologic types of ovarian tumors have been described, more than 90% of ovarian malignancies are epithelial tumors. Epithelial ovarian tumors start in the outer surface of the ovaries. Primary peritoneal cancer and fallopian tube cancer are similar to epithelial ovarian cancer and are treated in the same way. They can range from being benign to highly malignant. Epithelial ovarian cancer is the most common type of ovarian cancer. ''nothing will come from nothing''. Epidemiology there is a difference in frequen. The origin and pathogenesis of epithelial ovarian cancer has perplexed investigators for. Malignant ovarian tumor has the highest mortality rate among all gynecological cancers 1. Ovarian carcinogenesis, type i and type ii tumors, p53 mutation, kras, braf, pten, pik3ca mutations. Epithelial ovarian cancer (eoc) is the most common type of ovarian cancer 2.
Types Of Ovarian Tumors Ovarian Cancer Johns Hopkins Pathology
Ovarian Epithelial Stromal Tumors And Similar Lesions In The Testis Chapter 5 Gynecologic And Urologic Pathology. Epithelial ovarian cancer is the most common type of ovarian cancer. There are several types of benign epithelial tumors. Epithelial ovarian tumors start in the outer surface of the ovaries. Rare types of ovarian cancer include germ cell tumours (teratomas and dysgerminomas). Epithelial ovarian cancer (eoc) is the most common type of ovarian cancer 2. Epidemiology there is a difference in frequen. ''nothing will come from nothing''. Ovarian carcinogenesis, type i and type ii tumors, p53 mutation, kras, braf, pten, pik3ca mutations. Primary peritoneal cancer and fallopian tube cancer are similar to epithelial ovarian cancer and are treated in the same way. They can range from being benign to highly malignant. The origin and pathogenesis of epithelial ovarian cancer has perplexed investigators for. Malignant ovarian tumor has the highest mortality rate among all gynecological cancers 1. These tumors can be benign (not cancer), borderline (low malignant potential), or epithelial ovarian tumors that are benign don't spread and usually don't lead to serious illness. In general, the majority of eoc patients are diagnosed in advanced stage (stage iii or iv) disease, due to the. Epithelial ovarian cancer presents with a wide variety of vague and nonspecific symptoms, including the following although many histologic types of ovarian tumors have been described, more than 90% of ovarian malignancies are epithelial tumors.